As a long-time observer of vegan innovations, I’m continually amazed by the ingenuity driving advancements in plant-based choices. These developments are creating entirely new product categories that benefit our health, the environment, and animal welfare.
Let’s explore some of the most exciting breakthroughs in vegan technology, from lab-grown meat to biodegradable packaging, and examine their potential impact on various industries.
Cellular Agriculture: Growing Meat Without Animals
Cellular agriculture stands out as one of the most cutting-edge fields in vegan innovation. This technology allows for the production of real animal tissue from cells, eliminating the need for raising and slaughtering animals.

The Process
- Scientists extract stem cells from an animal through a harmless biopsy.
- These cells are placed in a nutrient-rich medium where they multiply and differentiate into muscle fibers.
- The resulting tissue is identical to conventional meat at a cellular level.
Benefits and Challenges
Cellular agriculture offers significant advantages over traditional livestock farming:
- Reduced land and water usage
- Lower greenhouse gas emissions
- Elimination of antibiotics in meat production
However, challenges continue. Scaling up production to meet global demand remains a hurdle, and the cost of lab-grown meat is still high.
Despite these obstacles, companies like Memphis Meats and Mosa Meat are making rapid progress, bringing us closer to seeing lab-grown meat on our plates.
Precision Fermentation: Brewing Animal-Free Proteins
Precision fermentation is another exciting area of vegan innovation. This process uses microorganisms like yeast or bacteria to produce specific proteins identical to those found in animal products.
How It Works
Take Perfect Day Foods as an example. They’ve used precision fermentation to create milk proteins without cows:
- The DNA sequence for cow’s milk protein is inserted into yeast.
- The yeast produces the protein through fermentation.
- The result is dairy-identical proteins used to make cheese, yogurt, and ice cream indistinguishable from their animal-derived counterparts.
This technology extends beyond dairy. Companies are using precision fermentation to produce everything from egg whites to collagen, opening up new possibilities for vegan choices across various industries.
From Lab to Table: Implementing Vegan Innovations
While the science behind these innovations is fascinating, the real challenge comes from bringing them to market. Let’s examine how some companies are turning these technologies into consumer products.
Case Study: Beyond Meat’s Plant-Based Revolution
Beyond Meat has become a household name in the plant-based meat choice space. Their success stems from meticulously engineering a product that mimics the taste, texture, and cooking properties of beef.
Ingredient Selection
Beyond Meat uses a combination of pea protein, coconut oil, and beet juice extract to copy the protein content, fat marbling, and color of beef.
Texture Engineering
Through a process of heating, cooling, and pressure, they create a fibrous texture that closely resembles muscle tissue.
Flavor Development
Natural flavors and spices are used to create a meaty taste profile.
Marketing Strategy
Beyond Meat positioned their products in the meat section of grocery stores, making them more accessible to curious omnivores.
The result is a product that appeals not just to vegans, but to meat-eaters looking to reduce their consumption of animal products.
Overcoming Challenges in Vegan Innovation
While the potential of vegan innovations is enormous, the path to widespread adoption faces several obstacles. Here are some common challenges and strategies to overcome them:
Consumer Acceptance
One of the biggest hurdles for many vegan innovations is gaining consumer acceptance. People are often skeptical of new foods, especially those produced using unfamiliar technologies.
Strategies to Overcome:
- Focus on Taste and Texture: Ensure that products are delicious and satisfying in their own right, not just as substitutes.
- Educate Consumers: Be transparent about production processes and the benefits of these new products.
- Target Flexitarians: Focus on consumers who are already open to reducing their animal product consumption.
Regulatory Hurdles
Novel food technologies often face regulatory challenges. For instance, lab-grown meat is still navigating the approval process in many countries.
Strategies to Address:
- Engage Early: Work with regulatory bodies from the early stages of product development.
- Provide Robust Safety Data: Conduct thorough safety testing and be prepared to share results with regulators and the public.
- Collaborate: Work with industry peers to establish standards and best practices.
Adapting Vegan Innovations to Different Scenarios
The versatility of many vegan innovations allows for adaptation to various scenarios:
Customized Nutrition
Precision fermentation and cellular agriculture allow for the creation of proteins with specific nutritional profiles. This technology could be used to create personalized foods tailored to individual dietary needs.
Sustainable Space Travel
Lab-grown meat and other vegan innovations could be crucial for long-term space missions, providing astronauts with fresh, nutritious food without the need for livestock.
Disaster Relief
Shelf-stable, nutrient-dense vegan foods could be invaluable in disaster relief efforts, providing essential nutrition in challenging circumstances.
From Basics to Mastery: Building on Vegan Innovation Knowledge
Understanding vegan innovations is just the beginning. To truly master this field, consider:
- Diving deep into the underlying sciences (biotechnology, food science, materials science).
- Exploring the business side of bringing innovations to market.
- Staying updated on regulatory developments and policy discussions.
- Experimenting with new products and technologies as they become available.
Practical Exercises to Reinforce Learning
To deepen your understanding of vegan innovations:
Compare and Contrast
Try a plant-based meat choice alongside it’s conventional counterpart. Note the similarities and differences in taste, texture, and cooking properties.
DIY Vegan Innovation
Experiment with making your own plant-based choices at home. Try creating a vegan egg substitute using aquafaba or a meat choice using textured vegetable protein.
Market Analysis
Visit your local grocery store and analyze the placement and marketing of vegan products. How are they positioned relative to conventional products?
Technology Deep Dive
Choose one vegan innovation technology (e.g., cellular agriculture) and create a detailed timeline of it’s development and key milestones.
Future Forecasting
Based on current trends, forecast what new vegan innovations we might see in the next 5-10 years. What challenges might they face?
The Future of Vegan Fashion
Vegan innovations extend beyond food into the realm of fashion. Designers and researchers are developing new materials that mimic the properties of animal-derived fabrics without the ethical concerns.
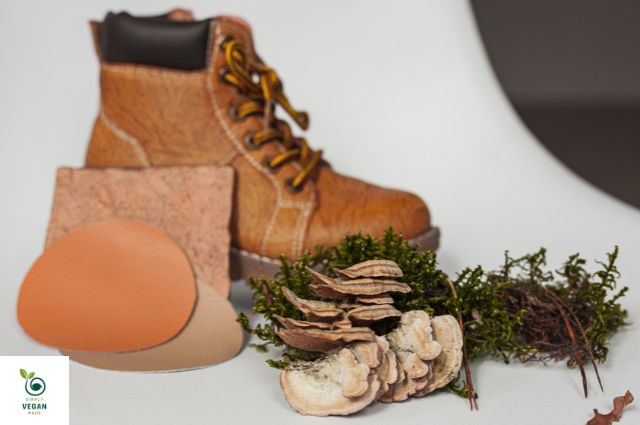
Plant-Based Leather Alternatives
Several companies are creating leather choices from plant materials:
- Piñatex: Made from pineapple leaf fibers, this material offers a sustainable choice to leather.
- Apple Leather: Created from apple waste, this material is being used in luxury fashion items.
- Mushroom Leather: Companies like Bolt Threads are developing leather-like materials from mycelium, the root structure of mushrooms.
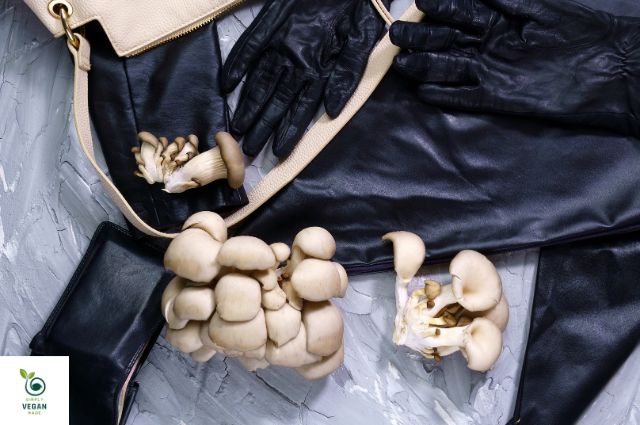
These materials offer similar durability and aesthetic appeal to animal leather while significantly reducing environmental impact.
Vegan Silk
Researchers have developed ways to produce silk-like fibers without silkworms:
- Spider Silk: Companies like Spiber are using genetically modified bacteria to produce spider silk proteins, which can be spun into fibers.
- Plant-Based Silk: Materials made from orange peels or soybeans are being developed as silk choices.
These innovations could alter the textile industry, offering cruelty-free choices to traditional silk.
Biodegradable Packaging Solutions
Vegan innovations are also addressing the global plastic pollution crisis through the development of biodegradable packaging materials.
Seaweed-Based Packaging
Companies like Notpla are creating packaging from seaweed that’s edible and biodegrades naturally in weeks.
Mushroom Packaging
Ecovative Design has developed packaging material from mycelium that can replace styrofoam and other non-biodegradable packaging materials.
Plant-Based Plastics
Researchers are developing plastics from materials like corn starch or sugarcane that biodegrade much faster than traditional petroleum-based plastics.
These innovations could significantly reduce the environmental impact of packaging waste.
The Role of AI in Vegan Innovation
Artificial Intelligence is playing an increasingly important role in vegan innovation:
Flavor Matching
AI algorithms are being used to analyze the molecular composition of animal products and find plant-based ingredients that can copy their flavors and textures.
Optimizing Formulations
Machine learning models can rapidly test thousands of ingredient combinations to improve plant-based product formulations for taste, texture, and nutritional profile.
Predicting Consumer Preferences
AI-powered market research tools can analyze trends and consumer data to forecast which vegan products are likely to succeed in the market.
The Impact of Vegan Innovations on Agriculture
The rise of vegan innovations is reshaping agricultural practices:
Shift in Crop Production
As demand for plant-based proteins increases, farmers are shifting towards growing more protein-rich crops like peas and lentils.
Vertical Farming
The need for consistent, high-quality plant ingredients is driving innovation in vertical farming technologies, allowing for year-round production of key ingredients.

Precision Agriculture
Advanced sensors and AI are being used to improve plant growth, reducing the need for pesticides and fertilizers.
The Economics of Vegan Innovation
The vegan innovation sector is attracting significant investment:
Venture Capital Interest
According to the Good Food Institute, investment in choice proteins reached $3.1 billion in 2020, more than tripling the previous year’s total.
Market Growth
The plant-based food market is projected to reach $74.2 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 11.9% from 2020 to 2027.
Job Creation
The vegan innovation sector is creating new job opportunities in fields like food science, biotechnology, and sustainable agriculture.
Vegan Innovations in Cosmetics and Personal Care
The beauty industry is also being transformed by vegan innovations:
Plant-Based Collagen
Companies are developing vegan choices to collagen using ingredients like algae or genetically modified yeast.
Cruelty-Free Testing Methods
Innovations in 3D tissue models and computer simulations are reducing the need for animal testing in cosmetics development.
Sustainable Packaging
Beauty brands are increasingly using recycled and biodegradable materials for packaging, reducing plastic waste.
The Role of Policy in Promoting Vegan Innovation
Government policies can play a crucial role in accelerating vegan innovation:
Research Funding
Increased public funding for research into plant-based and cellular agriculture technologies can speed up innovation.
Regulatory Frameworks
Developing clear regulatory guidelines for novel food technologies can provide certainty for investors and companies.
Tax Incentives
Offering tax breaks or subsidies for companies developing sustainable, plant-based products can encourage innovation.
The Global Impact of Vegan Innovations
Vegan innovations have the potential to address global challenges:
Food Security
Technologies like cellular agriculture and precision fermentation could help meet the growing global demand for protein without increasing land use.
Climate Change Mitigation
Plant-based and lab-grown choices to animal products could significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions from agriculture.
Water Conservation
Many vegan choices need less water to produce than their animal-based counterparts, potentially reducing strain on water resources.
The Future of Vegan Cuisine
Vegan innovations are a lot more influentual than about replicating animal products – they’re also inspiring new culinary creations:
Molecular Gastronomy
Chefs are using techniques from molecular gastronomy to create unique plant-based dishes with novel textures and flavors.
Fermentation Renaissance
There’s growing interest in traditional fermentation techniques to create complex, umami-rich vegan ingredients.
Algae-Based Foods
Algae are being explored as a sustainable source of protein and omega-3 fatty acids, opening up new culinary possibilities.
Ethical Considerations in Vegan Innovation
As vegan innovations advance, they raise new ethical questions:
GMO Debate
The use of genetically modified organisms in some vegan innovations has reignited debates about GMO safety and labeling.
Labor Practices
As the industry grows, ensuring fair labor practices throughout the supply chain becomes crucial.
Accessibility
There are concerns about whether these innovations will be accessible to all or stay luxury items for the wealthy.
The Role of Education in Advancing Vegan Innovation
Education plays a crucial role in the advancement and acceptance of vegan innovations:
STEM Education
Encouraging more students to pursue careers in food science, biotechnology, and related fields can drive future innovations.
Consumer Education
Educating consumers about the environmental and health benefits of vegan choices can increase adoption.
Culinary Training
Incorporating plant-based cooking techniques into culinary school curricula can help chefs create more appealing vegan options.
Collaborations Driving Vegan Innovation
Cross-industry collaborations are accelerating vegan innovation:
Food and Tech Partnerships
Partnerships between food companies and tech startups are bringing novel products to market faster.
Academic-Industry Collaborations
Universities are partnering with companies to conduct research and develop new technologies.
International Cooperation
Global collaborations are helping to share knowledge and resources, speeding up innovation worldwide.
The Role of Consumers in Vegan Innovation
Consumers play a crucial role in driving vegan innovation:
Demand Creation
Consumer demand for more sustainable and ethical products is a key driver of innovation in this space.
Feedback Loop
Consumer feedback on early products helps companies refine and improve their offerings.
Crowdfunding
Some vegan startups are using crowdfunding platforms to finance their innovations, allowing consumers to directly support projects they believe in.
Challenges in Scaling Vegan Innovations
As vegan innovations move from lab to market, several challenges in scaling up production emerge:
Supply Chain Development
Building reliable supply chains for novel ingredients can be challenging.
Manufacturing Processes
Developing efficient, large-scale manufacturing processes for new products often needs significant investment.
Quality Control
Maintaining consistent quality across large production runs can be difficult with novel ingredients and processes.
The Intersection of Vegan Innovation and Health
Vegan innovations are a lot more influentual than about sustainability – they also have potential health implications:
Nutrient Fortification
Many plant-based choices are fortified to match or exceed the nutritional profile of animal products.
Allergen-Free Options
Some vegan innovations are creating allergen-free choices to common allergens like dairy and eggs.
Gut Health
Fermented vegan products may offer probiotic benefits, supporting gut health.
The Role of Packaging in Vegan Innovation
Innovative packaging solutions are an integral part of vegan product development:
Edible Packaging
Some companies are developing edible packaging made from plant-based materials, reducing waste.
Active Packaging
Smart packaging technologies that extend shelf life are particularly important for fresh plant-based products.
Compostable Materials
Advances in compostable packaging materials are helping to reduce the environmental impact of vegan products.
The Future of Vegan Pet Food
Vegan innovations are extending to pet food:
Plant-Based Pet Foods
Companies are developing nutritionally complete plant-based pet foods, particularly for dogs.
Lab-Grown Pet Food
Cellular agriculture technologies are being applied to create animal protein for pet food without animal slaughter.
Insect-Based Pet Food
While not strictly vegan, insect-based pet foods offer a more sustainable choice to traditional meat-based options.
Vegan Innovations in Functional Foods
The intersection of vegan innovation and functional foods is creating new product categories:
Adaptogenic Beverages
Plant-based drinks infused with adaptogenic herbs are gaining popularity.
Probiotic-Rich Alternatives
Fermented plant-based products are being developed as choices to probiotic dairy products.
Protein-Fortified Snacks
Innovative snack foods are being fortified with plant proteins to appeal to health-conscious consumers.
The Role of Blockchain in Vegan Innovation
Blockchain technology is being applied to vegan innovations in several ways:
Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain can provide transparent tracking of ingredients from farm to table.
Verification of Vegan Claims
Blockchain-based systems can help verify and certify vegan and cruelty-free claims.
Tokenization of Vegan Startups
Some vegan startups are using blockchain-based tokens to raise funds and engage with their communities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the main drivers of vegan innovation?
Vegan innovation is primarily driven by concerns over animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and human health. The growing awareness of the environmental impact of animal agriculture, coupled with increasing interest in plant-based diets for health reasons, has spurred significant investment and research in this area.
How does cellular agriculture work?
Cellular agriculture involves growing animal cells in a controlled laboratory environment to produce meat, dairy, or other animal products without the need for whole animals. The process typically starts with stem cells, which are then cultured in a nutrient-rich medium to multiply and differentiate into the desired tissue type.
Are lab-grown meats considered vegan?
The vegan status of lab-grown meats is a topic of debate. While they don’t need animal slaughter, they do use animal cells in the initial stages.
Some vegans consider them acceptable as they significantly reduce animal suffering, while others prefer to avoid any product derived from animals.
What is precision fermentation?
Precision fermentation is a process that uses microorganisms like yeast or bacteria to produce specific proteins or other compounds. In the context of vegan innovation, it’s often used to create animal-free versions of proteins found in dairy, eggs, or other animal products.
How sustainable are plant-based meat alternatives?
Plant-based meat choices generally have a lower environmental impact than conventional meat. They typically need less land, water, and energy to produce, and generate fewer greenhouse gas emissions.
However, the exact sustainability profile can vary depending on the specific ingredients and production methods used.
Can vegan innovations help address global food security?
Vegan innovations have the potential to contribute to global food security by providing efficient, scalable sources of protein and other nutrients. Technologies like cellular agriculture and precision fermentation could produce large amounts of food with less land and resource use than traditional animal agriculture.
What are some challenges facing the vegan innovation industry?
Key challenges include scaling up production to meet demand, reducing costs to make products more accessible, overcoming regulatory hurdles for novel foods, and gaining consumer acceptance for new technologies and products.
How is AI being used in vegan food innovation?
AI is being used in various ways in vegan food innovation, including flavor matching to copy the taste of animal products, optimizing product formulations, predicting consumer preferences, and improving manufacturing processes.
What role does packaging play in vegan product innovation?
Packaging is a crucial aspect of vegan product innovation. Many companies are developing sustainable, plant-based packaging solutions to align with the environmental ethos of their products.
This includes biodegradable materials, edible packaging, and smart packaging technologies to extend shelf life.
How are vegan innovations impacting the agricultural sector?
Vegan innovations are driving changes in agriculture, including increased demand for plant protein crops, development of new crop varieties optimized for plant-based products, and advancements in vertical farming and precision agriculture technologies.
Key Takeaways
- Vegan innovations span a wide range of technologies, from cellular agriculture and precision fermentation to plant-based choices and sustainable packaging.
- These innovations are driven by concerns over animal welfare, environmental sustainability, and human health.
- Challenges in the field include scaling up production, reducing costs, navigating regulatory landscapes, and gaining consumer acceptance.
- The impact of vegan innovations extends beyond food into areas like fashion, cosmetics, and pet care.
- Emerging technologies like AI and blockchain are playing increasingly important roles in advancing vegan innovations.







